Africa is closer than ever to eradicating Polio – WHO
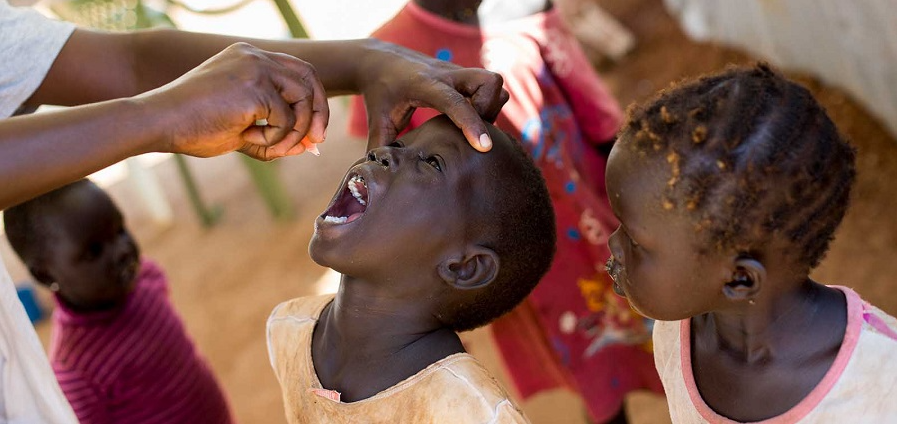
As the world marks World Polio Day, the World Health Organization (WHO) has emphasized that Africa is closer than ever to eradicating polio.
However, the organization’s Regional Director for Africa, Dr. Matshidiso Moeti, has urged for sustained efforts, stressing that significant work still lies ahead.
Moeti made this statement during her address for the 2024 World Polio Day on October 24, aimed at mobilizing global awareness and resources for the eradication of polio.
Progress marked by decades of collaboration
Reflecting on Africa’s journey towards a polio-free future, Dr. Moeti acknowledged the collaboration between governments, healthcare workers, and communities that have brought the continent to this pivotal point.
“This is not just a reflection on a decade of challenges and triumphs, but a meditation on the human spirit’s capacity to overcome adversity through shared purpose and commitment,” she said.
Milestones in 2024: A year of hope
In 2024, Africa achieved several key milestones in its fight against polio. Madagascar has now gone a full year without detecting circulating variant poliovirus type 1 (cVDPV1), and the wild poliovirus type 1 (WPV1) outbreak in Southern Africa, declared in 2022, has officially been closed.
Countries like Malawi, Mozambique, Tanzania, Zambia, and Zimbabwe, through coordinated efforts, have shown that joint action and community resilience are crucial to success.
Data from WHO revealed a 96% reduction in cVDPV1 detections across Africa between 2023 and 2024, while cVDPV2 detections dropped by 65%, further highlighting the impact of continuous vaccination efforts.
Challenges persist in the Lake Chad Basin and the Sahel
Despite these gains, challenges remain in regions like the Lake Chad Basin and the Sahel, where circulating variant poliovirus type 2 (cVDPV2) continues to spread.
Factors such as insecurity, limited healthcare access, and population displacement have hampered eradication efforts. As of September 2024, a total of 134 polio type 2 detections were reported across Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Chad, Mali, Niger, Nigeria, and the Central African Republic.
Dr. Moeti stressed the need for enhanced coordination in these regions. “Strong political commitment is crucial to the fight against polio. We must continue to work together, especially along borders, to eradicate this disease once and for all,” she urged.
Renewed collaboration and the way forward
In response to the ongoing threat, governments, WHO, UNICEF, and partners developed a coordinated plan in mid-2024 to eradicate variant poliovirus in high-risk areas.
As a result, nearly 70 million children in these regions have been vaccinated since the beginning of the year.
Vigilance remains critical, with Dr. Moeti advocating for increased surveillance and accelerated response efforts.
“We need to enhance surveillance, especially in underserved areas, and scale up high-quality vaccination campaigns,” she stated, emphasizing the need to act swiftly on any new detections.



